Bin Chicken
Bin Chicken is a tool that performs targeted recovery of low abundance metagenome assembled genomes through strategic coassembly.
It maximises recovery of novel diversity by automatically identifying sets of samples for coassembly and co-binning. In particular, it identifies groups of samples sharing novel marker genes that are predicted to have sufficient combined coverage for assembly and recovery of their associated genomes (10X minimum). Identical matching of sequence windows is used to reduce the risk of forming chimeric bins from near-relatives.
It is currently designed to use metagenomic data sequenced using Illumina short-read technology.
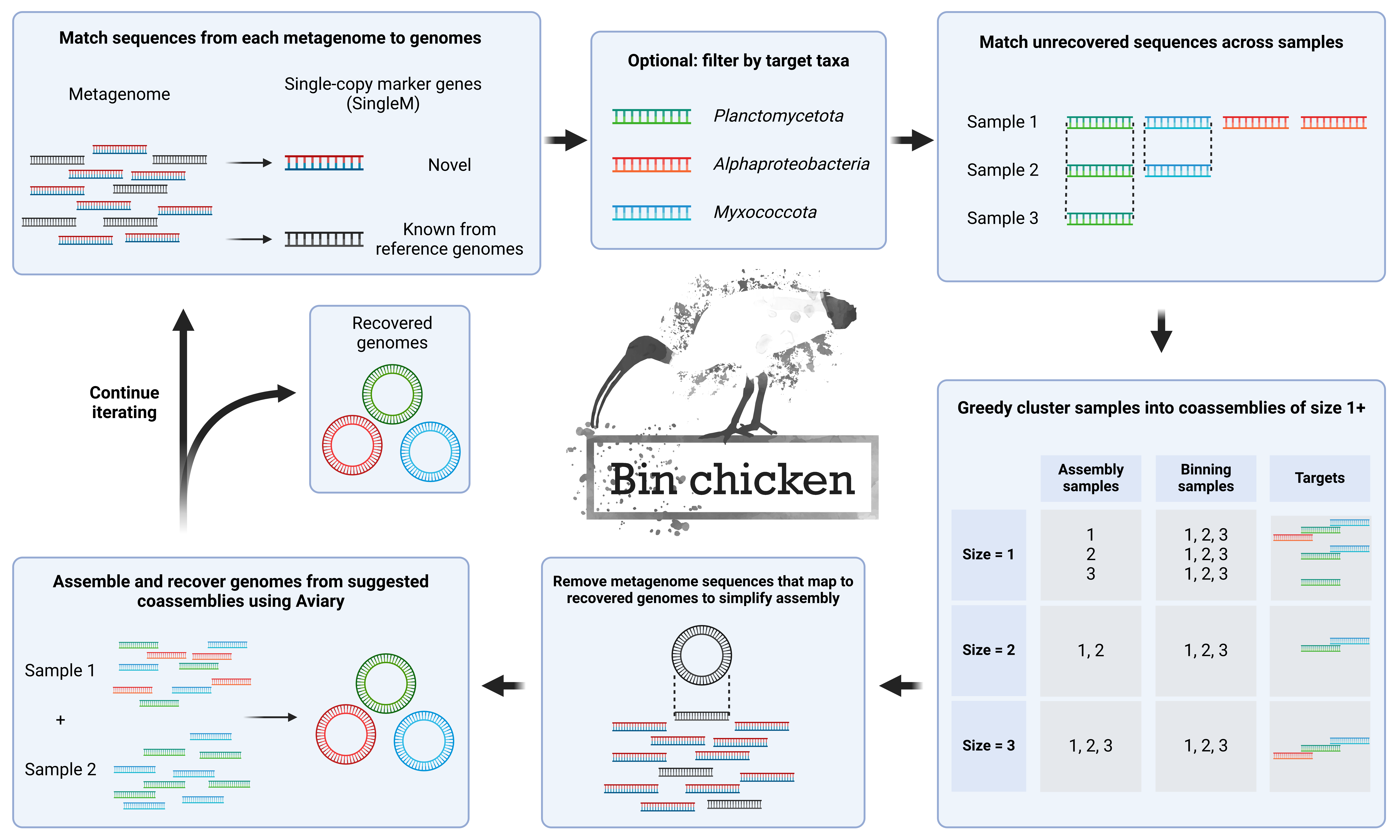
Example workflow
# Assemble and recover from each sample individually
# 20 samples used for differential abundance binning
binchicken single \
--forward-list samples_forward.txt --reverse-list samples_reverse.txt \
--run-aviary \
--cores 64 --output binchicken_single_assembly
# Assemble and recover from 2-sample coassemblies
# Prioritising samples with genomes not previously recovered
binchicken iterate \
--coassemble-output binchicken_single_assembly \
--run-aviary --cores 64 \
--output binchicken_2_coassembly
# Perform another iteration of coassembly, with 3-samples this time
binchicken iterate \
--coassembly-samples 3 \
--coassemble-output binchicken_2_coassembly \
--run-aviary --cores 64 \
--output binchicken_3_coassembly
Help
If you have any questions or need help, please open an issue.
License
Bin Chicken is licensed under GPL3 or later. The source code is available at https://github.com/AroneyS/binchicken.
Citations
Aroney, S.T.N., Newell, R.J.P., Tyson, G.W. and Woodcroft B.J. Bin Chicken: targeted metagenomic coassembly for the efficient recovery of novel genomes. Nat Methods (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-025-02901-1.
Bin Chicken is built on the SingleM tool, which is described in the following publication:
Woodcroft B.J., Aroney, S.T.N., Zhao, R., Cunningham, M., Mitchell, J.A.M., Nurdiansyah, R., Blackall, L. & Tyson, G.W. Comprehensive taxonomic identification of microbial species in metagenomic data using SingleM and Sandpiper. Nat Biotechnol (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02738-1.
If you use Aviary (through --run-aviary), please see the Aviary documentation for how to cite Aviary and its underlying dependencies.
Powered by Doctave
